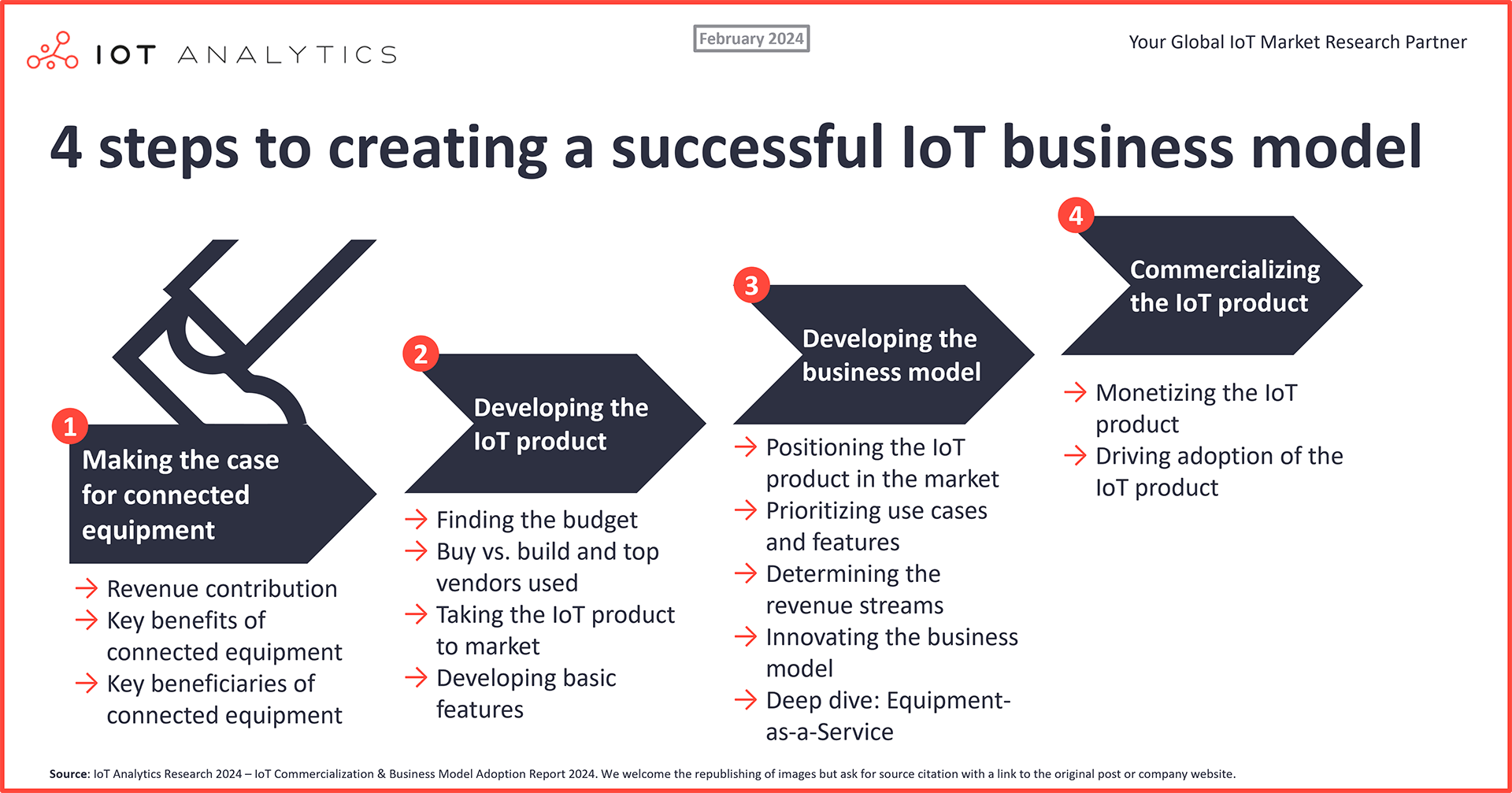
Understanding IoT Business Models
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing industries across the board, connecting devices and systems in unprecedented ways. This connectivity creates a wealth of opportunities for businesses to generate new revenue streams and optimize existing operations. However, to fully leverage the potential of IoT, it's crucial to understand the various IoT business models available and how they can be applied to specific industries and use cases.
Key IoT Business Models
Several distinct business models have emerged as popular approaches for monetizing IoT solutions. These models often overlap and can be combined to create unique and tailored strategies. Here are some of the most prominent:
1. Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Instead of selling a product outright, the PaaS model offers the product as a service, charging customers a recurring fee for its usage and maintenance. This model shifts the responsibility of upkeep and upgrades to the provider, offering convenience and predictable costs for the customer. Examples include smart lighting systems offered with monthly subscription, or connected industrial equipment where maintenance and performance monitoring are included in the service fee.
Benefits: Recurring revenue, increased customer loyalty, better product insights, and opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
2. Data Monetization
IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, which can be extremely valuable. This data can be anonymized, aggregated, and sold to third parties for various purposes, such as market research, trend analysis, or predictive modeling. For example, sensor data from connected cars can be used to improve traffic management or optimize insurance premiums.
Considerations: Data privacy and security are paramount. Businesses must ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA and implement robust security measures to protect user data.
3. Subscription-Based Model
This model charges customers a recurring fee for access to specific features, services, or data insights provided by the IoT solution. The subscription fee can vary based on the level of service, the number of users, or the amount of data consumed. A common example is a smart home security system with tiered subscription plans offering different levels of monitoring and support.
Advantages: Predictable revenue stream, strong customer relationships, and opportunities to offer premium features and services.
4. Outcome-Based Model
In this model, payment is tied to the achievement of specific outcomes or performance metrics. The customer only pays if the IoT solution delivers the desired results. For example, a connected agricultural system might charge based on the yield of crops, or an industrial energy management system might charge based on the amount of energy saved.
Challenges: Requires accurate measurement and monitoring of outcomes and may involve sharing risk with the customer.
5. Usage-Based Model
Customers are charged based on their actual usage of the IoT solution. This model is often used for services like cloud storage, data analytics, or network connectivity. The more the customer uses the service, the more they pay. This model is highly scalable and allows customers to pay only for what they need.
Example: A smart parking system charging per hour of parking, or a connected water meter charging based on water consumption.
6. Efficiency and Cost Savings
IoT solutions can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. Businesses can monetize these savings by offering services that help other companies optimize their processes. For example, a predictive maintenance solution can help reduce downtime and maintenance costs for industrial equipment.
Focus: Demonstrating quantifiable ROI and providing clear evidence of cost savings.
7. Licensing and White Labeling
Businesses can license their IoT technology or white-label their solutions to other companies. This allows them to expand their reach and generate revenue without having to directly manage the sales and marketing efforts. A software platform developed for IoT device management can be licensed to other companies to use under their own branding.
Benefits: Scalable revenue stream and reduced operational overhead.
IoT Revenue Streams
Beyond the specific business models, it's important to understand the different types of revenue streams that can be generated through IoT. These revenue streams often complement the chosen business model and can be combined to create a more comprehensive monetization strategy.
1. Hardware Sales
While many IoT business models focus on services, the initial sale of hardware devices remains a significant revenue stream. This includes sensors, gateways, and other connected devices. Focusing on high-quality, reliable hardware can differentiate your offering.
2. Software and Platform Fees
IoT platforms and software applications are essential for managing and analyzing data from connected devices. Revenue can be generated through licensing fees, subscription fees, or per-use charges for these platforms and applications.
3. Data Analytics and Insights
The insights derived from IoT data can be extremely valuable. Businesses can offer data analytics services to help customers understand their data and make better decisions. This can include custom reports, dashboards, and predictive modeling.
4. Integration and Customization Services
Integrating IoT solutions with existing systems and customizing them to meet specific needs can be a significant revenue stream. This includes consulting services, software development, and hardware customization.
5. Support and Maintenance
Providing ongoing support and maintenance for IoT solutions is essential for ensuring their reliability and performance. Revenue can be generated through service contracts, warranties, and remote monitoring services.
6. Value-Added Services
Offering additional services that enhance the value of the IoT solution can create new revenue streams. This can include training, consulting, security audits, and data privacy assessments.
Choosing the Right IoT Business Model and Revenue Stream
Selecting the most appropriate IoT business model and revenue stream depends on several factors, including the target market, the specific use case, the competitive landscape, and the company's capabilities. It's important to carefully consider these factors and develop a comprehensive monetization strategy that aligns with the overall business goals.
Factors to Consider:
- Target Market: Understand the needs and preferences of your target market and tailor your offering accordingly.
- Value Proposition: Clearly define the value that your IoT solution provides to customers.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyze the competitive landscape and identify opportunities to differentiate your offering.
- Scalability: Choose a business model that can scale as your business grows.
- Data Privacy and Security: Implement robust security measures to protect user data and comply with regulations.
- Partnerships: Explore potential partnerships to expand your reach and capabilities.
By carefully considering these factors and developing a well-defined monetization strategy, businesses can unlock the full potential of IoT and generate significant revenue streams.

0 Comments